Climate Adaptation
In signing support for TCFD, the Chairman & CEO of AUO specifically mentioned in the statement that

Facing climate emergency, the greatest challenge of sustainable development, AUO is proud to support climate-related financial disclosures and transparency, and strengthen stakeholder trust for the Company's sustainable development. That is why we would like to play a part in the low carbon economy, respond to the opportunities and the challenges of the energy transition by developing a solar energy business, and applying our core technologies to improve the resilience of the human lifestyle and value chain creation.
AUO TCFD Framework




Climate Risk and Opportunity Analysis Matrix
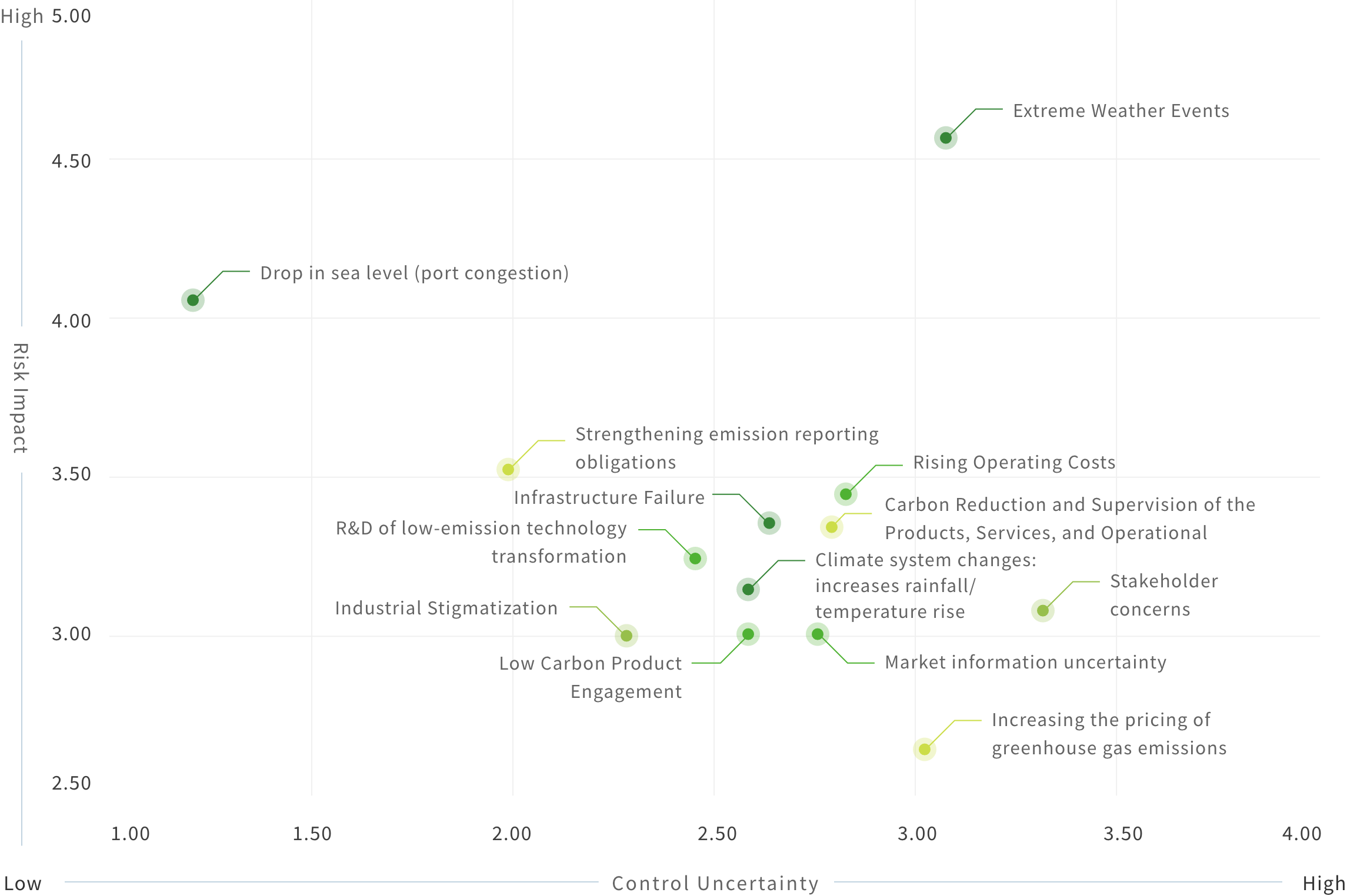
Quantification of Financial Impact of Climate Change Risk
Based on past climate risk identification results, AUO evaluated four major risks, including "product carbon footprint, market product competition, sustainable operations, and regulatory compliance," and conducted a quantitative assessment of financial impact with reference to the methodologies disclosed by domestic and foreign companies
| Risk | Financial quantification considerations | Assessment methods |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction of product carbon footprint | Impact on the European market, leading to revenue decline | Set short, medium, and long-term goals until 2025, estimating carbon reduction from 5% to 10% to 20%. Continuously focus on material reduction, improving equipment efficiency to decrease electricity consumption, and utilizing low-carbon energy to achieve additional carbon reduction value. |
| Market product competition | Impact on company orders, leading to revenue decline |
|
| Continuous operations (e.g., Flood risk) | Impact on production capacity and increased costs due to personnel attendance overtime/transportation costs and water truck dispatch costs |
|
| International initiatives and regulatory compliance | Financial costs arising from compliance with international initiative targets and regulations under low-carbon transition |
|
The results of climate risk and opportunity nancial impact assessments as a percentage of annual turnover