Supporting the Circular Economy through Recycling
To realize the sustainable re-use of resources and move beyond a linear economic model of manufacturing, production and disposal, the AUO waste disposal principle now embraces the promotion of the circular economy. Re-use within the production process is prioritized to reduce the use of raw materials, followed by recycling with incineration and landfill only if necessary to ensure the effective utilization and circulation of resources.
Waste output and waste reduction goals
Unit:metric tons
Trend chart of the waste reduction
Tracking waste management obligation properly
A waste disposal contractor audit plan is formulated by AUO every year to manage waste after they are removed from the plant. Pro-active audits of all waste contractors verify their management practices and track them after disposal to ensure that they are properly disposed of.
| Waste Type | Treatment Method | Recycled Product |
|---|---|---|
| Sludge | Heat treatment or solidification | Controlled low strength materials (CLSM) |
| Clear glass | Crushin | Additive for concrete and asphalt |
| HF liquid waste and dust | Chemical treatment | Industrial-grade sodium hexafluoro silicate |
| Indium dust and indium epoxy | Electrolysis | Indium ingot |
| Empty container | Washing and physical treatment | Plastic pellets |
| Etchant | Distillation | Industrial-grade phosphoric acid |
| Mixed metals | Crush and magnetic sorting | Metal recycling |

Stripper re-use
Purification recycling system inside factory
Waste solvent as auxiliary fuel
Looking for diverse reuse applications


A new business model that turns copper into gold
Innovative thinkings to coorperate with inter-industries
Stripper re-use
Purification recycling system inside factory
- A Stripper Recycle System (SRS) was installed within the plant.
- Waste liquid from the production process is distilled to remove contaminants
after adjustments to the concentration.and then used in the production process again
- Use of new liquid is reduced to accomplish the goal of resource recycling
Separation principle
Separation is achieved by exploiting the different boiling points of substances
- PR:No volatile component
- H.B.:High boiling point component
- L.B.:Low boiling point componen

Waste solvent as auxiliary fuel
Looking for diverse reuse applications
- waste disposal contractor was introduced to recover waste solvents for re-use instead of sending them directly to the incinerator.
- High heat value of waste solvents can be exploited through combustion to generate steam.
- The electrical energy generated by running steam through steam turbines can be supplied to businesses or sold to Taipower.
- This case not only reduced the environmental burden but also achieved great savings on incineration costs.

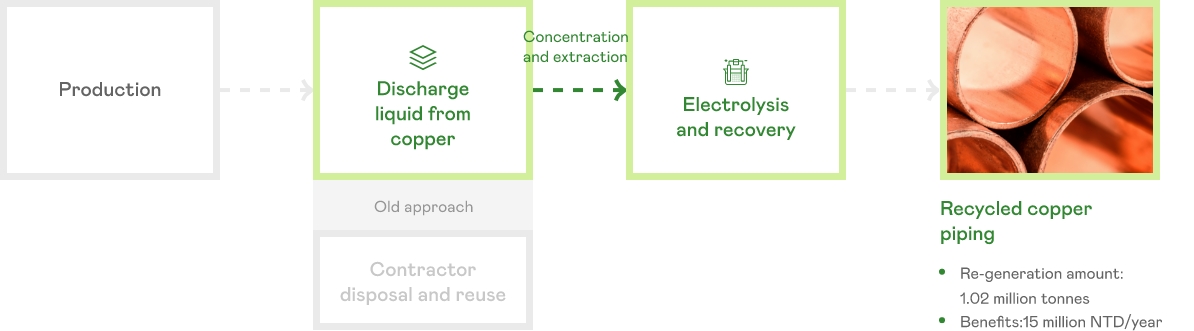
A new business model that turns copper into gold
Innovative thinkings to coorperate with inter-industries
- A first for the panel industry pioneered by AUO Houli plant
- Waste liquid containing copper from the etching process is processed using electrolysis into high-purity copper piping for use in other industrial applications.
- Benefits included a reduction in the amount of copper-rich waste liquid, a reduction in carbon emissions from transportation, and the prevention of pollution from copper flow.
- Value is added and the old linear economic model is converted into a renewable, circular economic model. Treatment costs are reduced and circular value is added through the sale of copper piping.