Materiality Assessment Process
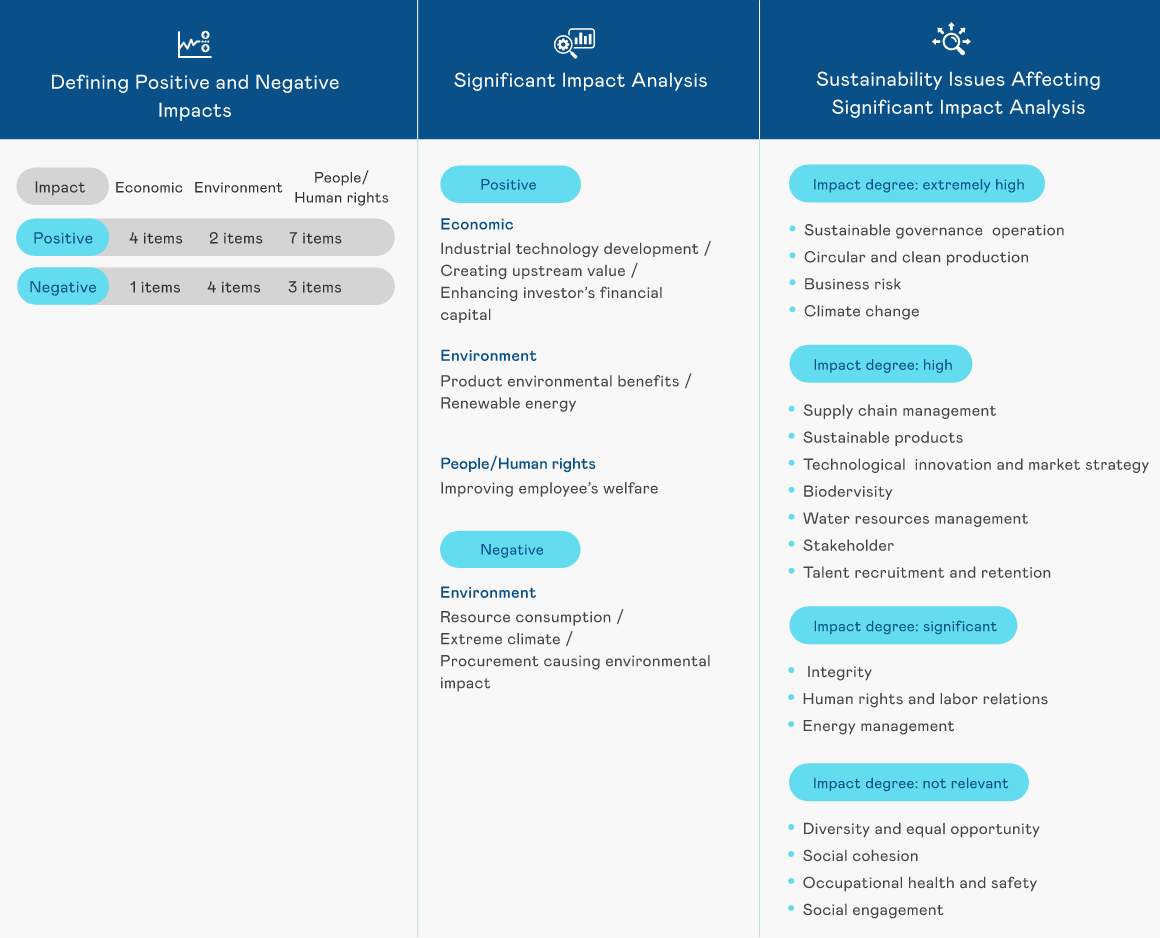
Assessing the relevance of issues based on global sustainability trends and GRI guidelines involves using surveys to understand stakeholders' concerns regarding the company's environmental, social (including human rights), and corporate governance aspects. A dual materiality assessment method is established to evaluate the operational impact of ESG issues on the company, with key partners in the company's value chain. External sustainability development impacts are evaluated based on the GRI Universal Standards 2021, integrating methodologies developed by the Value Balancing Alliance and the Harvard Business School's Impact-Weighted Accounts research project. This framework constructs an impact-based analysis process to identify material topics.
AUO Sustainability Impact Valuation Report
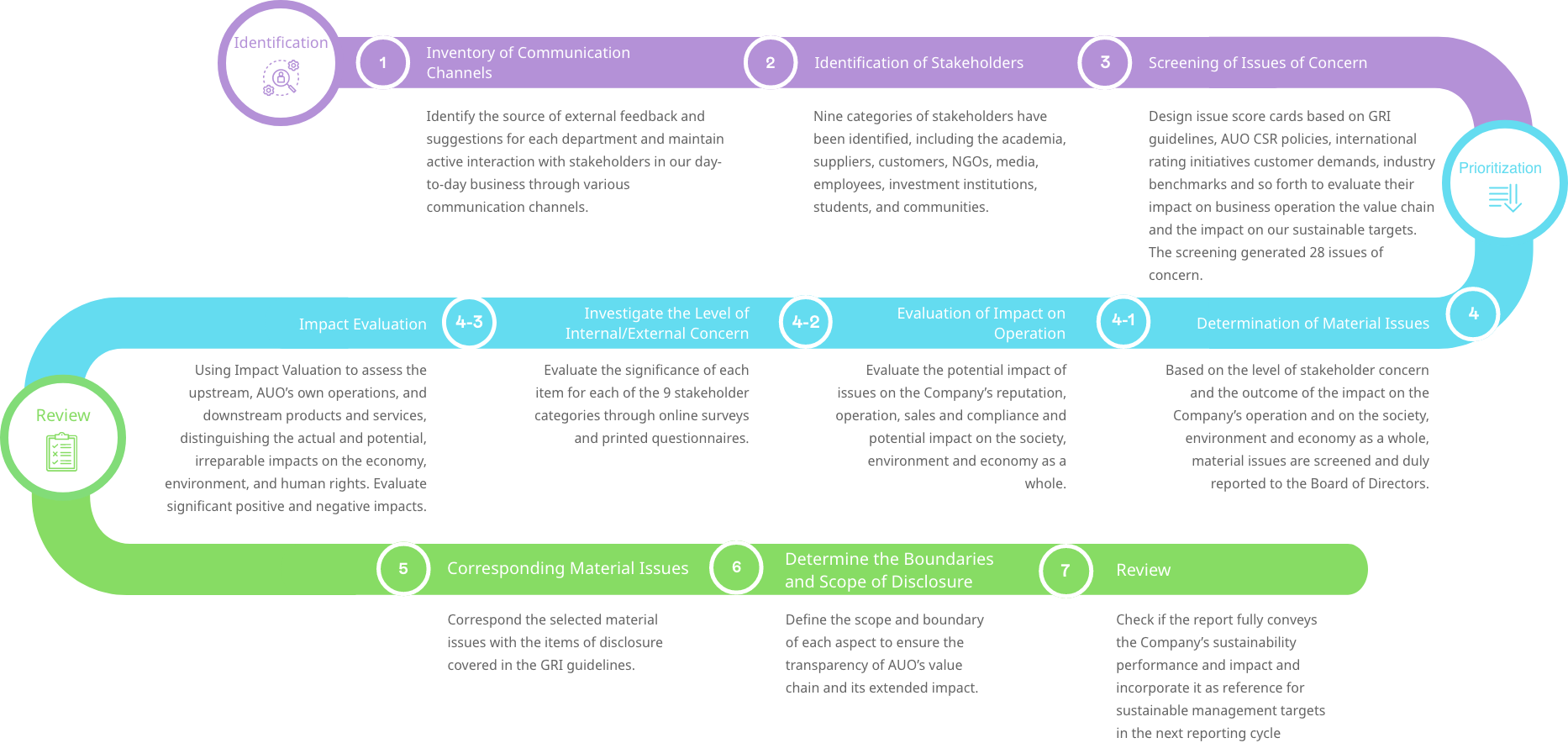
Risk Impact Assessment Process
Identification and Analysis of Material Issues for 2025
Double Materiality at AUO
| 2025 Materials issues |
Business Cases | Business Impact(Company Values) | Sustainability Impact (External Impact) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | Customer Satisfaction | Operating Risk | Employee Cohesion | Industry Technology Development(Positive) | Creation of Upstream Value(Positive) | Investor Financial Capital(Positive) | Environmental Benefit of Product(Positive) | Increase in Renewable Energy(Positive) | Improvement of Employee Life and Welfare(Positive) | Consumption of Energy Resource(Negative) | Environmental Impact of Purchasing(Negative) | Extreme weather (Negative) | ||
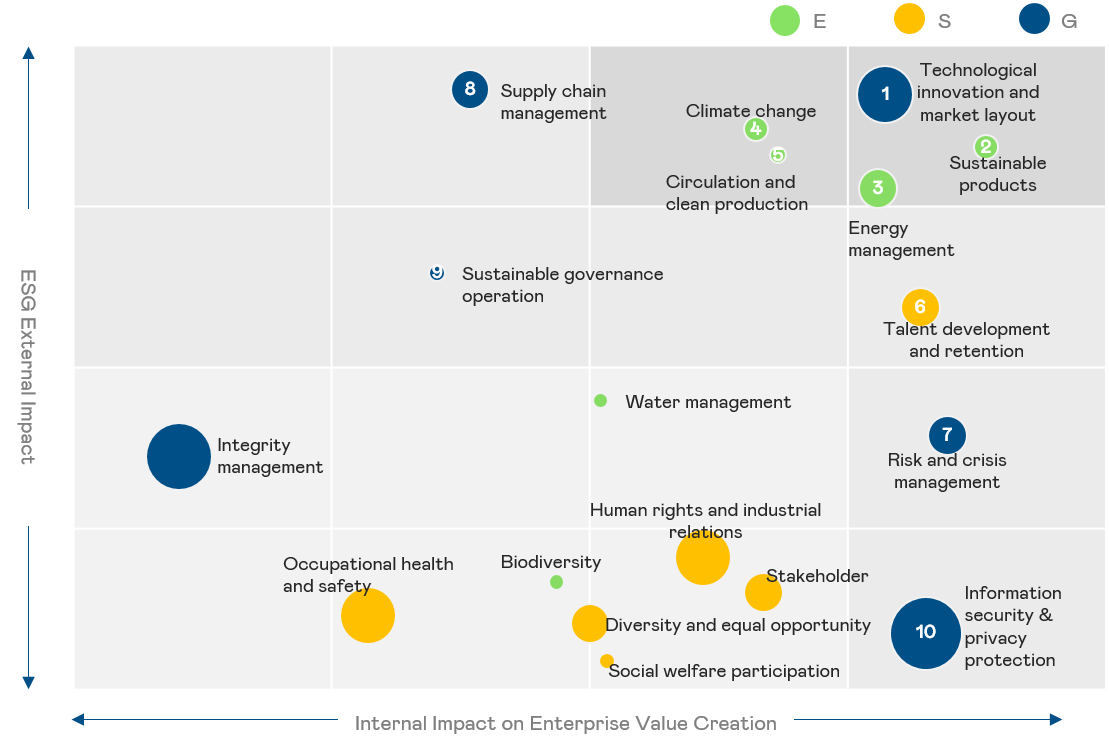
| Sustainability Governance Operations | Everyone from the Board, senior management to all employees can effectively implement the goals and vision in a systematic manner to reduce the impact of risks,strengthen business resilience, and realize the sustainable management of the Company. | |||||||||||||
| Technological Innovation and Market Strategy | The definition of strategies for product management, product management, market strategy, and new business development as well as the introduction of R&D technology and innovative techniques are revenue generation and essential the competitiveness of the Company. | |||||||||||||
| Risk and crisis management | Effective risk monitoring and management to increase the resilience of the Company and win market trust. | |||||||||||||
| Supply Chain Management | Suppliers are important partners. A risk and sustainability management mechanism must be established to reduce the procurement cost, and achieve inclusive growth with supplier partners to build a resilient supply chain. | |||||||||||||
| Information security & privacy protection | Effectively prevent the leakage of confidential information, ensure business continuity and competitiveness, and avoid financial loss and brand damage caused by security incidents. | |||||||||||||
| 2025 Materials issues |
Business Cases | Business Impact(Company Values) | Sustainability Impact (External Impact) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | Customer Satisfaction | Operating Risk | Employee Cohesion | Industry Technology Development(Positive) | Creation of Upstream Value(Positive) | Investor Financial Capital(Positive) | Environmental Benefit of Product(Positive) | Increase in Renewable Energy(Positive) | Improvement of Employee Life and Welfare(Positive) | Consumption of Energy Resource(Negative) | Environmental Impact of Purchasing(Negative) | Extreme weather (Negative) | ||
| Circular and Clean Production | The use of innovative technologies for waste reduction and recycling can help reduce the impact of production and open up new business opportunities. | |||||||||||||
| Sustainable Product | Having the design and innovation capability to develop green products and services or rigorous green material certification and conflict mineral management mechanisms will help win customer trust, premium price opportunity and boost environmental friendliness. | |||||||||||||
| Climate Change | Faced with the diverse and complex effects of climate change, engage in suitable mitigation and adaptation behaviors, think about life cycle management, and identify risks and opportunities. | |||||||||||||
| Energy Management | Green upgrades in energy prices and renewable energy use will lead to significantly higher manufacturing costs. Low-carbon production and energy management will generate opportunities for intelligent services. | |||||||||||||
| 2025 Materials issues |
Business Cases | Business Impact(Company Values) | Sustainability Impact (External Impact) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | Customer Satisfaction | Operating Risk | Employee Cohesion | Industry Technology Development(Positive) | Creation of Upstream Value(Positive) | Investor Financial Capital(Positive) | Environmental Benefit of Product(Positive) | Increase in Renewable Energy(Positive) | Improvement of Employee Life and Welfare(Positive) | Consumption of Energy Resource(Negative) | Environmental Impact of Purchasing(Negative) | Extreme weather (Negative) | ||
| Talent development and retention | Providing employees with fair and comprehensive compensation, benefits, and competency training will reduce turnover, boost recruitment, and increase profitability | |||||||||||||